In recent years, the study of male fertility has become increasingly nuanced, with new biomarkers and indices being developed to provide deeper insights into male reproductive health. One such marker that has gained significant attention is the DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI). This index measures the amount of damaged DNA in sperm and serves as a critical indicator of male fertility potential. Understanding the DFI, its implications, and how it can be managed is crucial for individuals and couples navigating fertility challenges.
What is the DNA Fragmentation Index?
DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI) is a measure of the percentage of sperm with fragmented or damaged DNA. DNA fragmentation refers to the presence of breaks or irregularities in the DNA strands within the sperm cell. These breaks can occur in the form of single-strand or double-strand breaks, both of which can impact the sperm’s ability to fertilize an egg successfully.
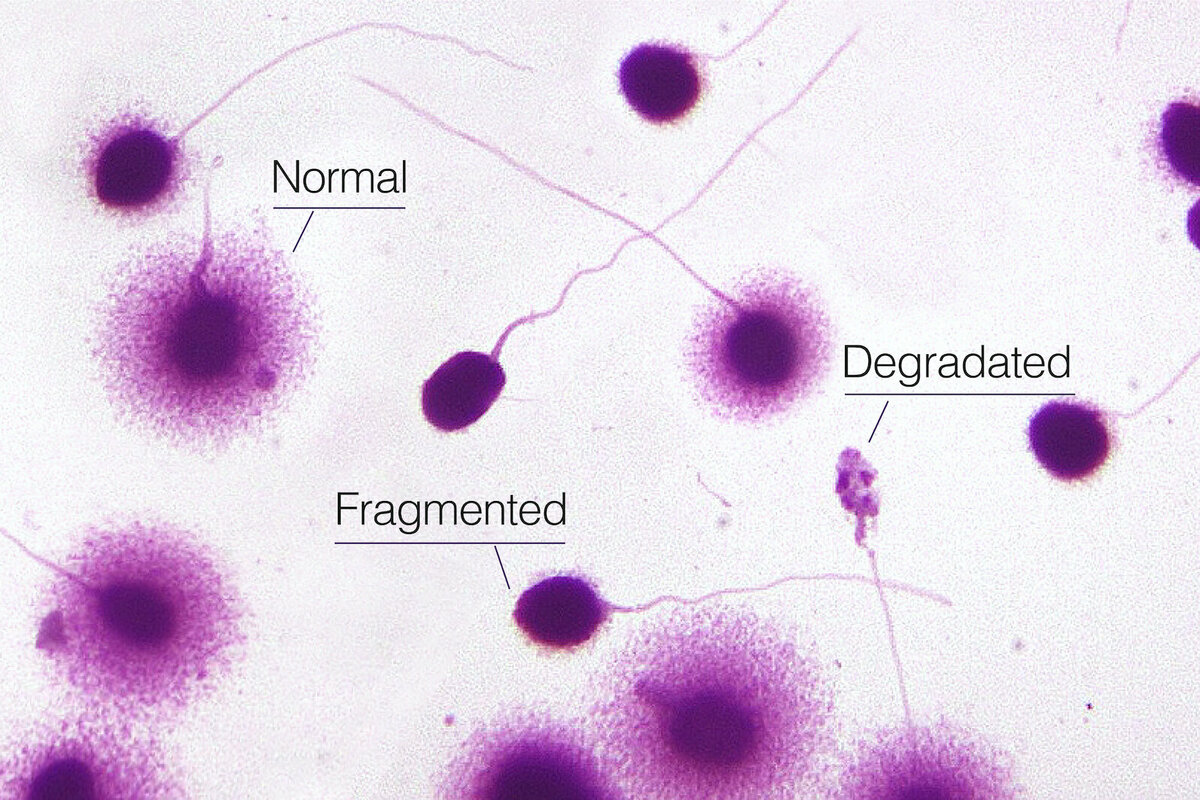
Why is DFI important?
The integrity of sperm DNA is essential for successful fertilization and healthy embryo development. High levels of DNA fragmentation in sperm can lead to several reproductive issues, including:
- Reduced Fertility: High DFI levels are associated with lower fertility rates. Damaged DNA can impair the sperm’s ability to penetrate and fertilize the egg.
- Miscarriages: Elevated DFI is linked to an increased risk of miscarriages, as fragmented DNA can result in genetic abnormalities in the embryo.
- Poor Embryo Quality: Even if fertilization occurs, embryos derived from sperm with high DNA fragmentation may have lower viability and poorer developmental outcomes.
- Failed Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART): Higher DFI levels can negatively impact the success rates of ART procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Causes of DNA Fragmentation

Several factors can contribute to increased DNA fragmentation in sperm. These include:
- Oxidative Stress: An imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidants in the body can lead to oxidative stress, which damages sperm DNA.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of exercise can all contribute to higher DFI levels.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to pollutants, pesticides, and other environmental toxins can adversely affect sperm DNA integrity.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as varicocele (enlargement of veins within the scrotum), infections, and chronic illnesses can increase DNA fragmentation.
- Aging: As men age, the quality of sperm tends to decline, leading to higher levels of DNA fragmentation.
Measuring DNA Fragmentation Index
DFI is typically measured through specialized laboratory tests that assess the extent of DNA damage in sperm samples. The most commonly used methods include:
- TUNEL Assay: The Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) assay detects DNA strand breaks by labeling the fragmented ends of DNA with fluorescent markers.
- SCSA (Sperm Chromatin Structure Assay): This assay uses flow cytometry to measure the susceptibility of sperm DNA to denaturation, which indicates the presence of fragmented DNA.
- COMET Assay: Also known as Single Cell Gel Electrophoresis, this assay measures DNA strand breaks by evaluating the migration pattern of DNA fragments under an electric field.
- SCD (Sperm Chromatin Dispersion) Test: This test evaluates the dispersion of sperm chromatin after the removal of nuclear proteins, with higher dispersion indicating higher levels of DNA fragmentation.
Interpreting DFI Results
DFI results are typically expressed as a percentage, representing the proportion of sperm with fragmented DNA. The interpretation of these results can vary, but generally:
- DFI < 15%: Considered low DNA fragmentation, indicating good sperm DNA integrity.
- DFI 15-25%: Moderate DNA fragmentation, suggesting a potential risk for fertility issues.
- DFI > 25%: High DNA fragmentation, is associated with significant fertility challenges and a higher likelihood of reproductive complications.
Strategies to Improve DNA Fragmentation Index
For individuals with elevated DFI, several strategies can be employed to improve sperm DNA integrity:
- Antioxidant Therapy: Antioxidants such as vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and Coenzyme Q10 can help reduce oxidative stress and improve sperm DNA integrity.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption, can positively impact DFI levels.
- Environmental Management: Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants can help protect sperm DNA from damage.
- Medical Treatment: Treating underlying medical conditions, such as varicocele, infections, or hormonal imbalances, can improve DNA fragmentation.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques: In cases where natural conception is challenging, ART procedures such as IVF with ICSI can be utilized to select the best quality sperm, potentially bypassing the issues associated with high DFI.
The Role of Clinicians and Fertility Specialists

Clinicians and fertility specialists play a crucial role in the management of DNA fragmentation in male patients. They are responsible for:
- Assessment and Diagnosis: Conducting thorough assessments to determine the presence and extent of DNA fragmentation.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Develop tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs and DFI levels.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about the impact of lifestyle, environmental factors, and medical conditions on sperm DNA integrity.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Regularly monitoring DFI levels and making necessary adjustments to treatment plans to optimize fertility outcomes.
Conclusion
The DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI) is a vital marker in the realm of male fertility, providing valuable insights into sperm DNA integrity and its implications for reproductive health. High levels of DNA fragmentation can pose significant challenges to fertility, increasing the risk of infertility, miscarriages, and poor embryo quality. However, with appropriate assessment, lifestyle modifications, and medical interventions, it is possible to improve DFI levels and enhance fertility outcomes. For individuals and couples facing fertility issues, understanding and addressing DNA fragmentation can be a critical step toward achieving successful conception and healthy pregnancies.
As research in this field continues to evolve, the importance of DFI and its role in male fertility will undoubtedly become even more pronounced. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take control of their reproductive health and work towards overcoming the challenges posed by DNA fragmentation.

